
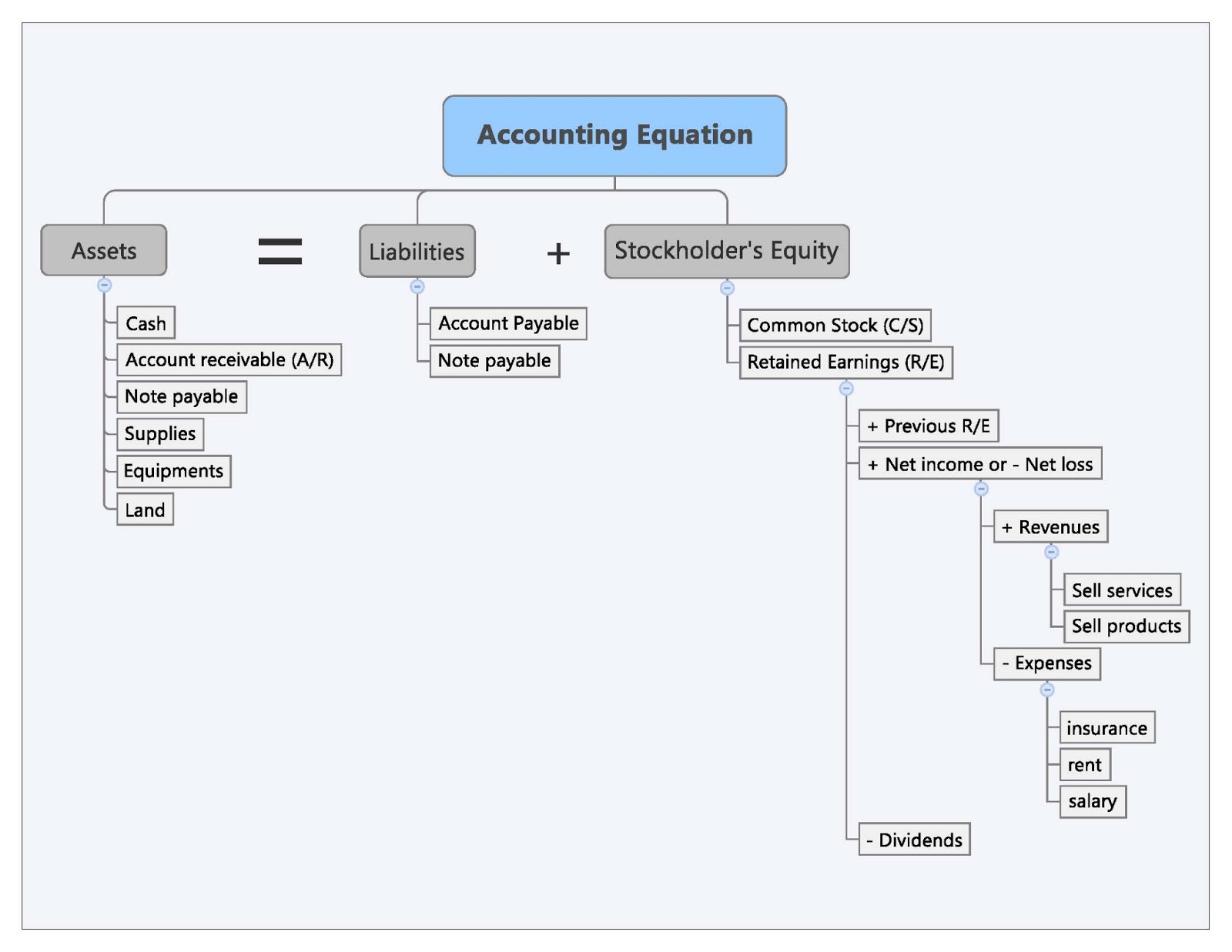
In the above transaction, Assets increased as a result of the increase in Cash. At the same time, Capital increased due to the owner’s contribution. Remember that capital is increased by contribution of owners and income, and is decreased by withdrawals and expenses. As business transactions take place, the values of the accounting elements change.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
As this is not really an expense of the business, Anushka is effectively being paid amounts owed to her as the owner of the business (drawings). Required Explain how each of the above transactions impact the accounting equation and illustrate the cumulative effect that they have. An asset can be cash or something that has monetary value such as inventory, furniture, equipment etc. while liabilities are debts that need to be paid in the future.
What is the difference between an asset and a liability?
Based on the data in the previous section, here’s the journal entry to record the payment of the accrued December rent in January. Metro Corporation collected a total of $5,000 on account from clients who owned money for services previously billed. During the month of February, Metro Corporation earned a total of $50,000 in revenue from clients who paid cash. This transaction also generates a profit of $1,000 for Sam Enterprises, which would increase the owner’s equity element of the equation. At this time, there is external equity or liability in Sam Enterprise.
A company has assets totaling $50,000 and equity of $20,000. What are their liabilities?
We’re going to call them current assets and current assets are going to be cash or anything that can be converted into cash in less than 1 year, okay? So typical things that we see in current assets claim these “above are going to be cash. We’re going to see accounts receivable, money that’s owed to us by our customers, inventory, right? Things that we’re going to convert into cash pretty soon within 1 year.
- Let’s take a look at the formation of a company to illustrate how the accounting equation works in a business situation.
- The difference between revenues and expenses results in net income or loss.
- The cost of this sale will be the cost of the 10 units of inventory sold which is $250 (10 units x $25).
- After calculating the owner’s equity with the formula above, you should plug it into the accounting equation and make sure the equation balances.
- The accounting equation ensures that a company’s balance sheet remains balanced.
After the company formation, Speakers, Inc. needs to buy some equipment for installing speakers, so it purchases $20,000 of installation equipment from a manufacturer for cash. In this case, Speakers, Inc. uses its cash to buy another asset, so the asset account is decreased from the disbursement of cash and increased by the addition of installation equipment. Now that we have a basic understanding of the equation, let’s take a look at each accounting equation component starting with the assets. Shareholders’ equity is the total value of the company expressed in dollars. Put another way, it is the amount that would remain if the company liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its debts. The remainder is the shareholders’ equity, which would be returned to them.
The difference between the sale price and the cost of merchandise is the profit of the business that would increase the owner’s equity by $1,000 (6,000 – $5,000). On 1 January 2016, Sam started a trading business called Sam Enterprises with an initial investment of $100,000. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
Journal entries often use the language of debits (DR) and credits (CR). A debit refers to an increase in an asset or a decrease in a liability or shareholders’ equity. A credit in contrast refers to a decrease in an asset or an increase in a liability or shareholders’ equity.
The income statement reports the revenues, gains, expenses, losses, net income and other totals for the period of time shown in the heading of the statement. If a company’s stock is publicly traded, earnings per share must appear on the face of the income statement. The accounting equation is the backbone of the accounting and reporting system. It is central to understanding a key financial statement known as the balance sheet (sometimes called the statement of financial position).
In accounting, the claims of creditors are referred to as liabilities and the claims of owner are referred to as owner’s equity. The accounting equation is fundamental to the double-entry accounting system. Every financial transaction impacts at least two accounts, maintaining the balance. The shareholders’ equity number is a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities. In this form, it is easier to highlight the relationship between shareholder’s equity and debt (liabilities).